By Dr. Surveen Ghumman Sindhu: In vitro fertilization (IVF) is an assisted reproductive technique that involves fertilization of the oocyte (egg) by sperm outside of the woman’s body. The embryos are cultured in sterile plastic dishes.
IVF was initially developed for patients with absent or damaged fallopian tubes. It is now offered as a treatment for many types of infertility when other methods fail. Standard IVF combines oocytes from the woman and sperm from the man in the laboratory with the goal of obtaining fertilization. If fertilization occurs, the resulting embryo or embryos are placed into the woman’s uterus two to three days later. Pregnancy occurs in approximately 50 percent of women after IVF.
Step 1 – Pre IVF tests:
Both partners must have blood tests prior to beginning the process. There may be other tests required of the woman if they have not been done during the infertility workup. Men must have a semen analysis to evaluate the number and quality of the sperm. A psychologist consults prior to beginning IVF should be done.
Step 2 – Ovarian Stimulation and Monitoring:
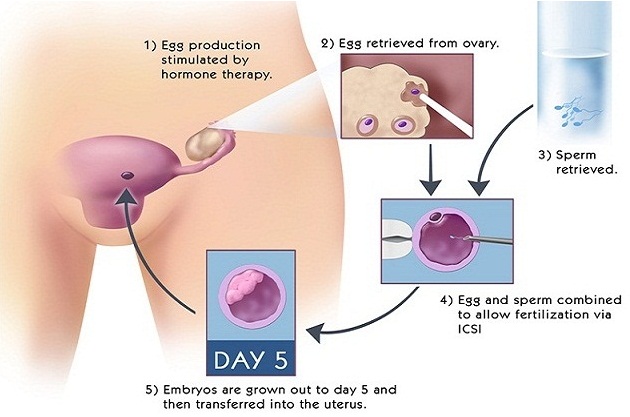
After all testing is completed; a baseline ultrasound examination of the ovaries will be done to check for cysts or other pelvic abnormalities. If no problems are found, daily hormonal injections are given to regulate the growth of and to increase the number of mature ovarian follicles, which contain the oocytes. Your progress is monitored by blood tests that evaluate the level of estradiol, a hormone produced by the follicles, and by ultrasound, which measures the number and size of ovarian follicles. When the follicles have reached the appropriate stage, an injection of HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is given to cause final maturation and loosening of the oocyte within the follicle. Oocyte retrieval is scheduled after this injection.
Step 3 – Oocyte Retrieval:
Egg retrieval is a surgical procedure performed in an operating room. An anesthetist will be present during the procedure and will give you general anesthesia. During the egg retrieval procedure, a needle, along with an ultrasound probe, is inserted in the vagina. The needle will be gently moved into each mature follicle in the ovaries. The fluid contained within each ovarian follicle is aspirated and sent to the laboratory where it is examined for the presence of an oocyte. The egg retrieval procedure usually takes about 15-20 minutes, depending on the number of mature follicles present.
The eggs are placed in a special dish in an incubator for a minimum of three hours prior to insemination. On the day of the egg retrieval, the male partner will need to produce a sperm specimen for the IVF lab to use to fertilize the eggs. The man providing the semen should abstain from ejaculation for two to five days before the egg retrieval. Oocytes obtained are inseminated with the sperm isolated from this semen specimen several hours after retrieval. Some women experience light vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal pain after egg retrieval.
Some women experience light vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal pain after egg retrieval. Starting the day of egg retrieval, progesterone supplements in the form of an injection or vaginal capsules form. This helps to prepare the uterine lining for attachment of the embryos. This medication will need to be continued until the day of pregnancy testing.
Sometimes no oocytes are retrieved, or oocytes may not fertilize; or once fertilized, may not develop as embryos.
Step 4 – Fertilization and Embryo Transfer:
The morning after the oocyte retrieval, each oocyte will be examined for signs of fertilization. About two-thirds of normal oocytes will fertilize and will have two small internal structures called pronuclei.
Embryo transfer is scheduled about 48 to 72 hours after retrieval. Blastocyst transfer is done on fifth day when the cleavage stage embryo becomes a blastocyst. Embryos are placed into the uterus via a small catheter passed through the cervix. No more than three embryos will be replaced. Any embryos in excess of the number to be replaced can be cryopreserved (frozen) for later use. The pregnancy test will be done 14 days after embryo replacement.
Intra-cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI):
Sperm microinjection (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) or ICSI was developed mainly to treat severe male infertility which includes very low sperm counts, low motility or other sperm abnormalities.
This technique consists of the insertion of one sperm inside the ovum. In order to undergo ICSI, a couple must follow the same steps as for IVF.
ICSI allows many infertile couples whose only prior choice was between insemination with donor sperm or adoption to become the biological parents of their children.
Microsurgical Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (MESA):
The surgical removal of sperm from the testis or from the epididymis (the collecting tubes attached to the testicle) is performed in the operating room for men with no sperms in their ejaculate. A surgical microscope is used to allow the surgeon to open and aspirate the tiny tubules containing sperm. This procedure is usually done in combination with IVF or ICSI.